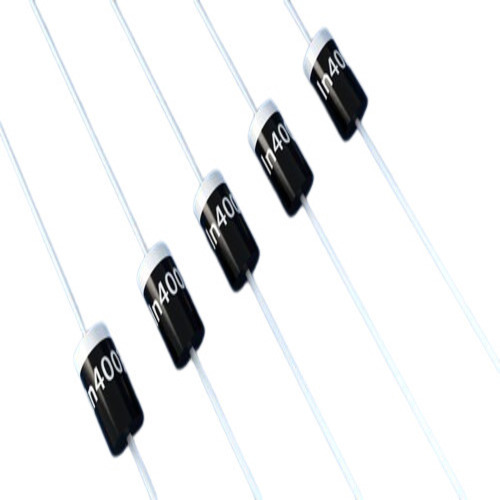
Electronic Diodes
Price 150 INR/ Pair
Electronic Diodes Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 10 Pieces
- Payment Terms
- Cash Advance (CA), Cash in Advance (CID), Cheque
- Main Domestic Market
- Maharashtra
About Electronic Diodes
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that allows electric current to flow in only one direction. It acts as a one-way switch, conducting current when voltage is applied in the "forward" direction (from anode to cathode) and blocking it in the "reverse" direction. This property is fundamental to many applications, such as rectifying alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) and protecting circuits.
How it works
Anode and cathode: A diode has two terminals: an anode (positive) and a cathode (negative).
Forward bias: When the anode is more positive than the cathode, the diode is "forward-biased" and conducts current.
Reverse bias: When the anode is more negative than the cathode, the diode is "reverse-biased" and blocks current.
P-N junction: Diodes typically achieve this one-way conduction through a p-n junction, a boundary between p-type and n-type semiconductor materials.


Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry



 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS Call Me Free
Call Me Free